Female pattern baldness, although less commonly discussed than its male counterpart, is a significant concern for many women.
Characterized by thinning of hair on the scalp, female pattern baldness can have emotional and psychological effects, impacting self-esteem and confidence.
Understanding the causes and available treatment options is crucial for women dealing with this condition.
What Causes Female Pattern Baldness?
Female pattern baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia, shares similarities with male pattern baldness but manifests differently in women. Here are some key factors contributing to female pattern baldness:
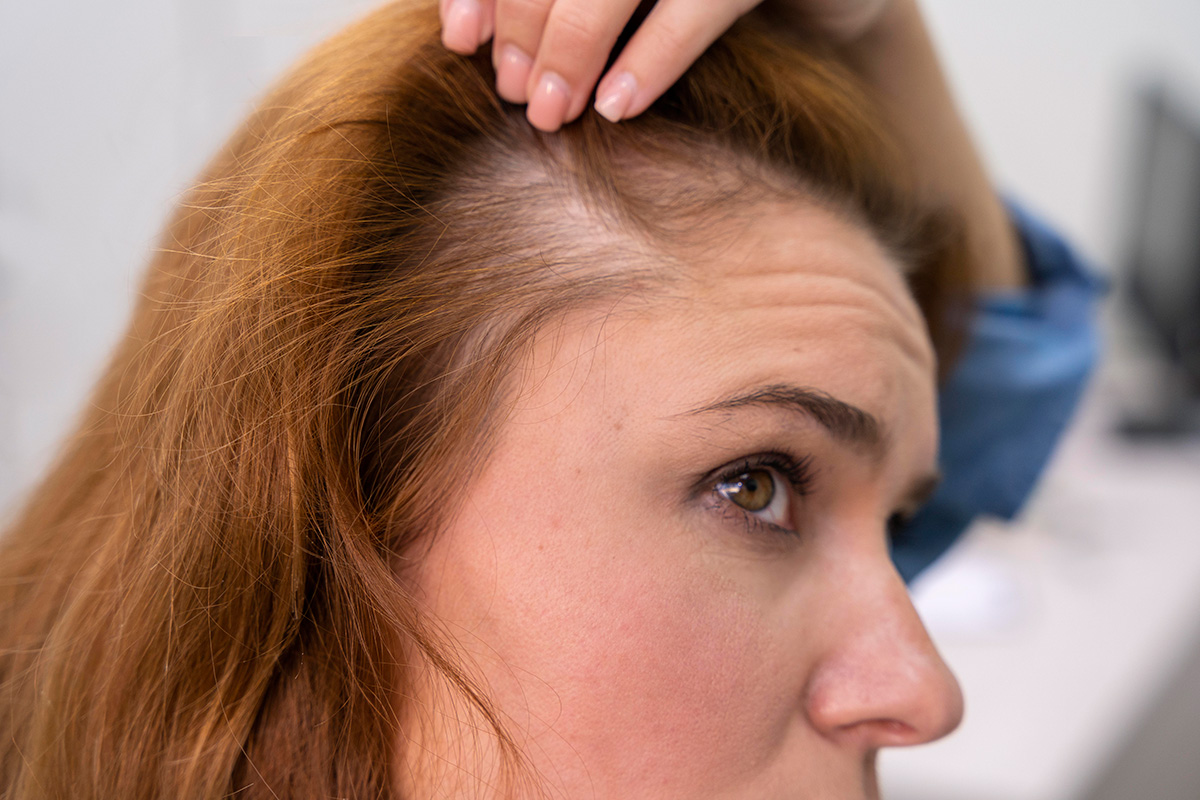
- Genetics: Just like in men, genetics play a significant role in female pattern baldness. Women with a family history of hair loss are more likely to experience thinning hair themselves.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly changes in androgen levels, can contribute to female pattern baldness. Androgens are male hormones present in both men and women, but when levels become imbalanced, they can affect hair follicles and lead to hair loss.
- Age: Female pattern baldness often becomes more noticeable with age, typically starting around menopause. However, hair thinning can occur at any age and may progress gradually over time.
- Medical Conditions and Medications: Certain medical conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, and autoimmune diseases can contribute to hair loss in women. Additionally, medications used to treat these conditions may also have hair loss as a side effect.
Treatment Options for Female Pattern Baldness:
While female pattern baldness cannot be fully reversed, several treatment options can help slow down hair loss and promote regrowth:
- Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter minoxidil (Rogaine) is the only FDA-approved topical treatment for female pattern baldness. Minoxidil works by stimulating hair follicles and prolonging the growth phase of the hair cycle. It is typically applied directly to the scalp once or twice daily.
- Prescription Medications: In some cases, healthcare providers may prescribe medications such as spironolactone or oral contraceptives to help regulate hormone levels and minimize hair loss.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP therapy involves injecting the patient’s own platelet-rich plasma into the scalp to stimulate hair growth. While research on its effectiveness is ongoing, some women have reported positive results with this treatment.
- Hair Transplantation: In advanced cases of female pattern baldness, hair transplantation may be considered a surgical option. This procedure involves transplanting hair follicles from donor areas to thinning or balding areas of the scalp.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle by eating a balanced diet, managing stress levels, and avoiding harsh hair treatments can help support overall hair health and minimize further hair loss.
Conclusion:
Female pattern baldness can be a distressing condition for many women, but there are treatment options available to help manage and address hair loss. By consulting with a dermatologist or hair restoration specialist, women can explore personalized treatment plans tailored to their specific needs and concerns. Remember, addressing female pattern baldness is not just about restoring hair — it’s about reclaiming confidence and feeling comfortable in your own skin.


